Integration of New Games
Objective
‘There is a multitude of mHealth applications that aim to solve societal health problems by stimulating specific types of physical activities via gamification. However, physical health activities cover just one of the three World Health Organization (WHO) dimensions of health. The novel notion of Unified Health Gamification (UHG) is to cover besides physical health also social and cognitive health and well-being. In fact, according to the WHO, it is even too restrictive to only consider physical activities: “Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being”
UHG is based on the following principles: (1) people should be capable to form teams with peers regardless of differences in health interests, (2) people should receive positive feedback at the personal level as well as on the level of their team, and (3) the implementation should be flexible with regards to the rules of health games (A. Shahrestani, 2017).’
GameBus is the first UHG application which enables the integration to third activity applications and wearables as well as games.
The goal is to enable the integration of interactive games so that game developers can log GameBus activities from their game’s events.
GameBus design allows us to define a game as an activity. This means that every successful game event can be saved as an activity. Game Rules can also be defined as “Challenge Rules” including “Property Conditions”. An additional advantage is a database service GameBus provides. In the following sections, the “Crossword” game is used as an example to ensure that these definitions are explained well and the integration of other new games can be done more easily consequently.
Crossword as an Integrated Game
Crossword is used for the illustration purposes to show how an example mini game is integrated in the GameBus. In order to play the game, one can add an activity/gameSession of type “crossword” and start playing. However, a challenge should be available to play a rewarded game where user can gain points according to the defined challenge rules.
Challenge Rules
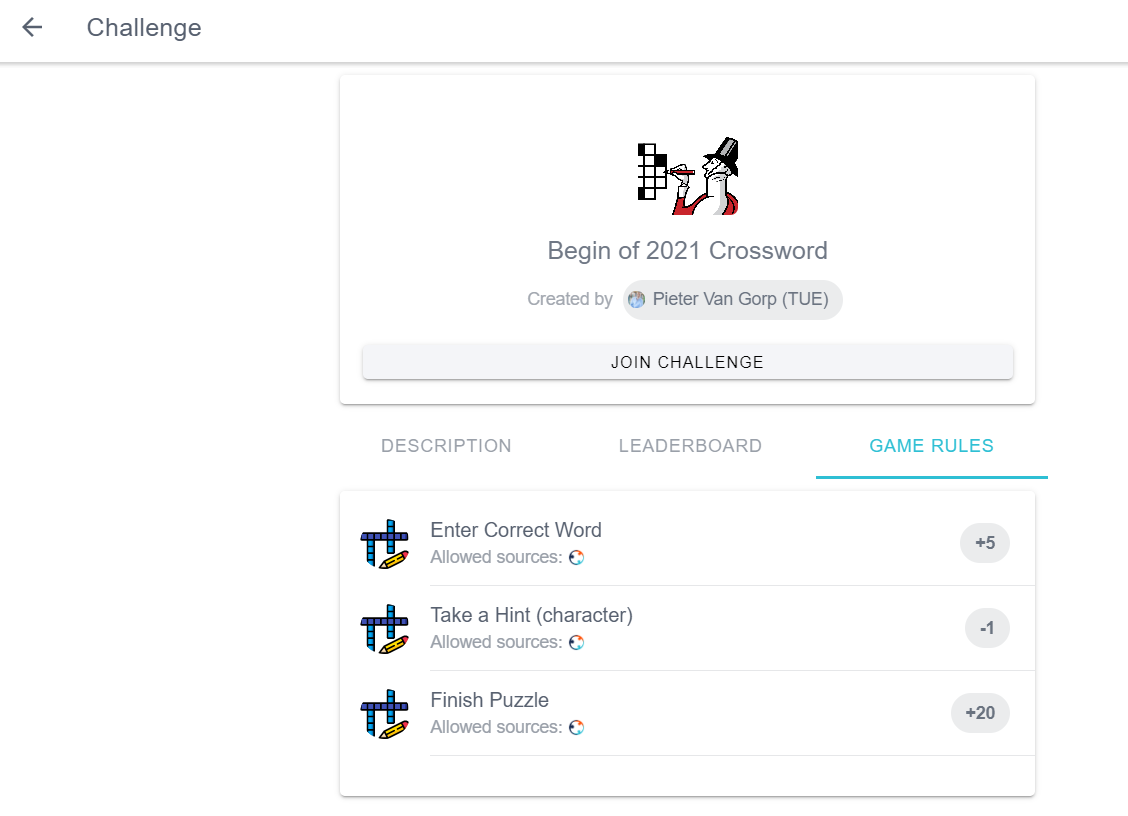
Challenge rules serve as the game rules. When creating the challenge, rules and conditions of the rules can be defined. These challenges are then listed under the “Rewarded activities” tab in the create activity page. These rules are thoroughly explained in the following section of “Crossword Walkthrough”. In the following picture rules of an example challenge “Begin of 2021 Crossword” are shown.
Crossword Walkthrough
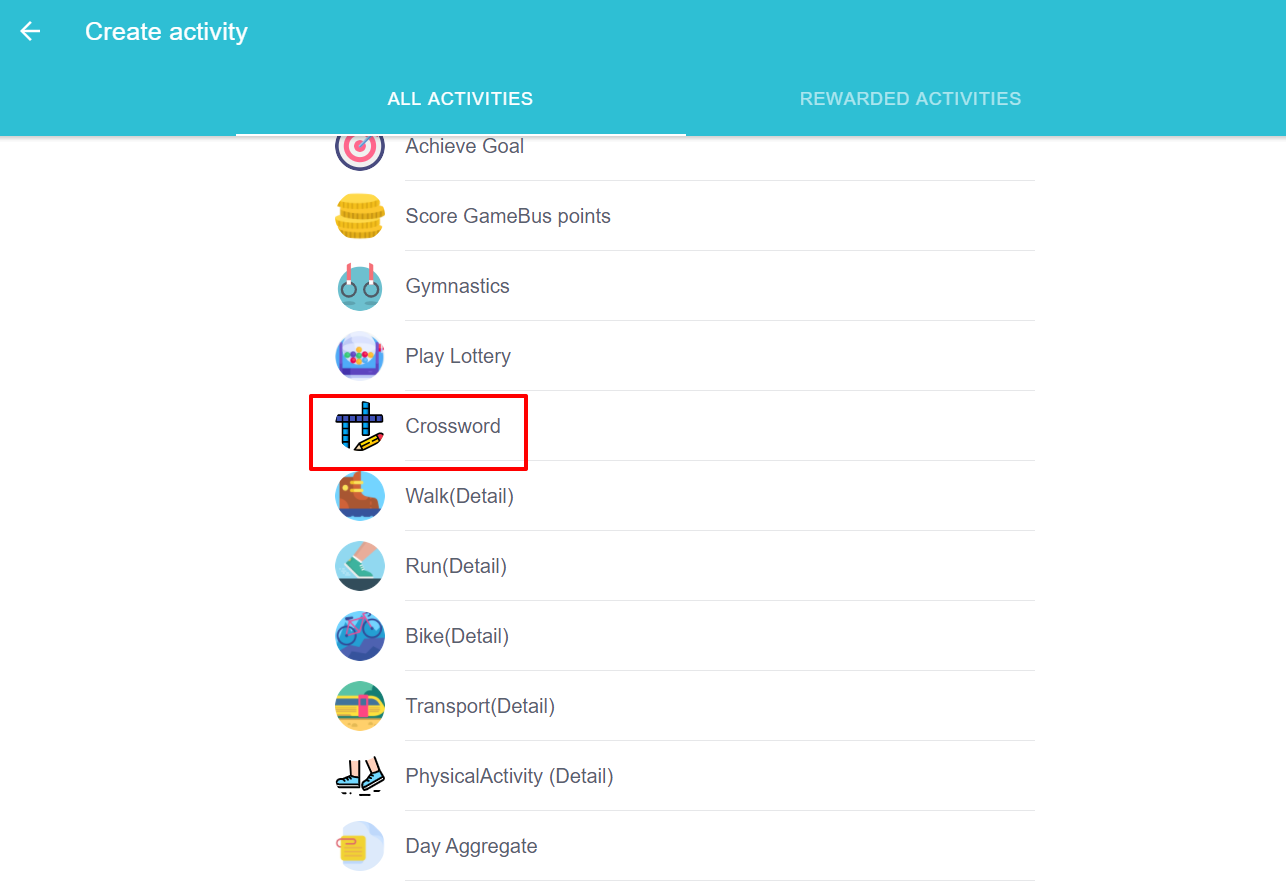
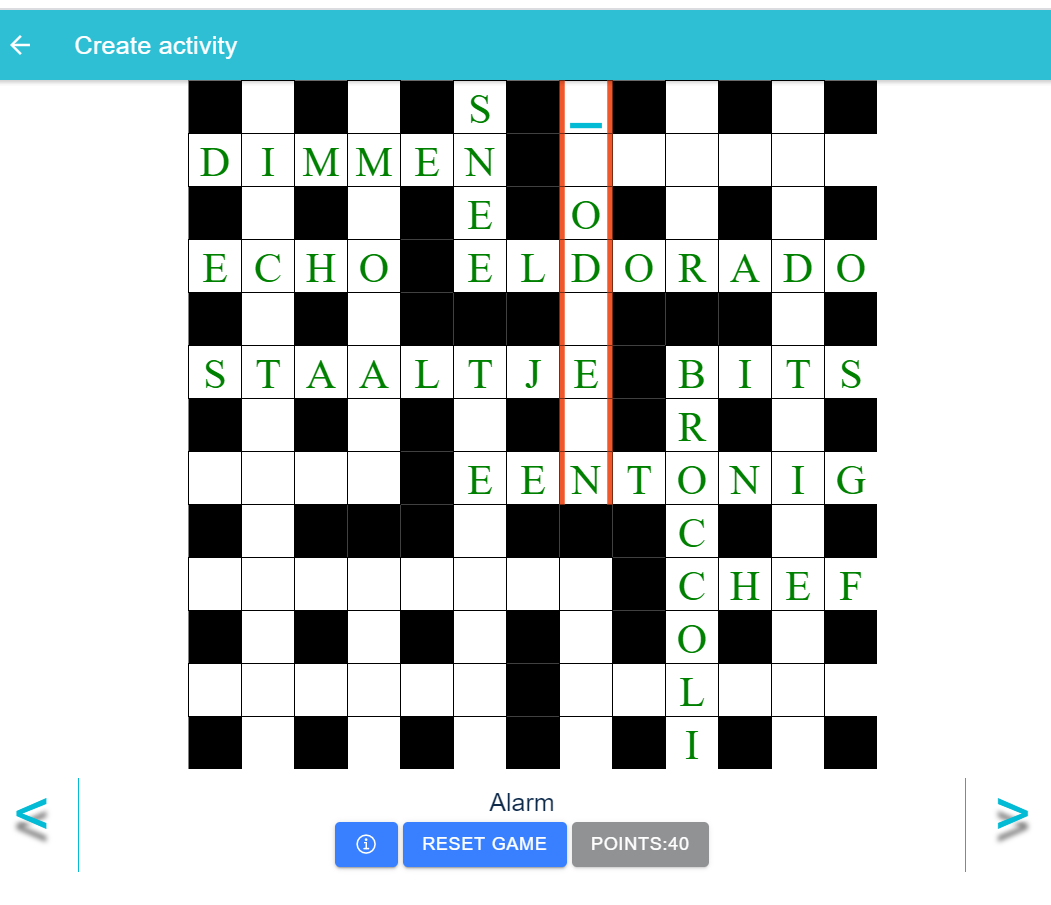
An unrewarded game activity can be created by choosing “crossword” from all activities menu as it is shown in the picture.
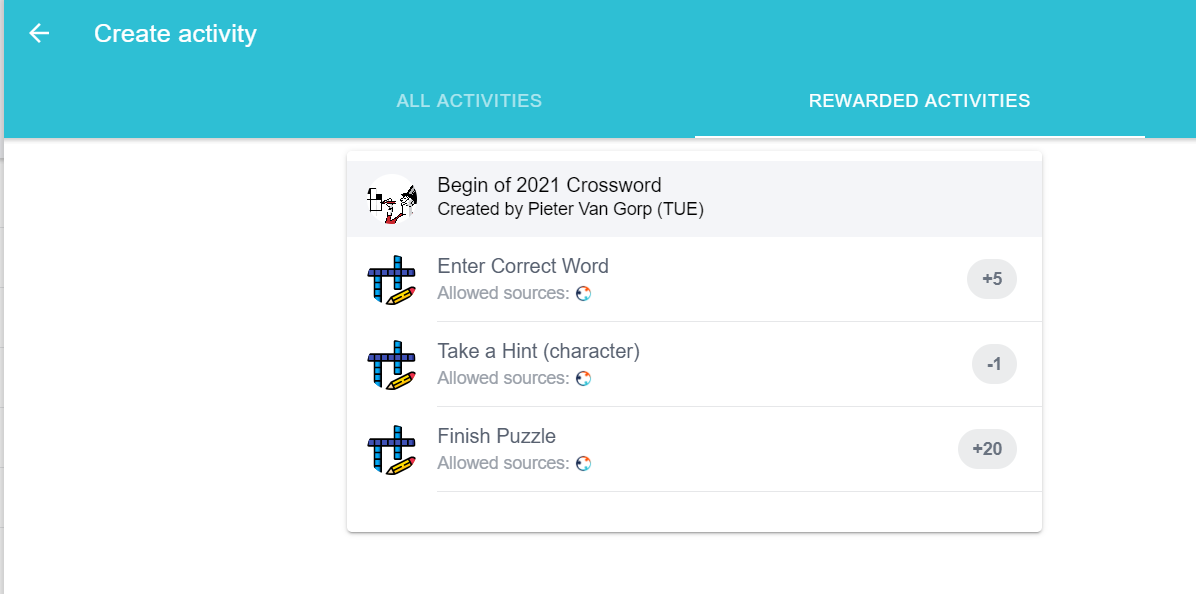
Game activity can also be created within the challenge and in this case it will be a rewarded activity which means it changes the balance points of the player with respect to the defined rules.
As mentioned earlier, game rules can be defined as challenge rules. In this example, 3 rules are defined:
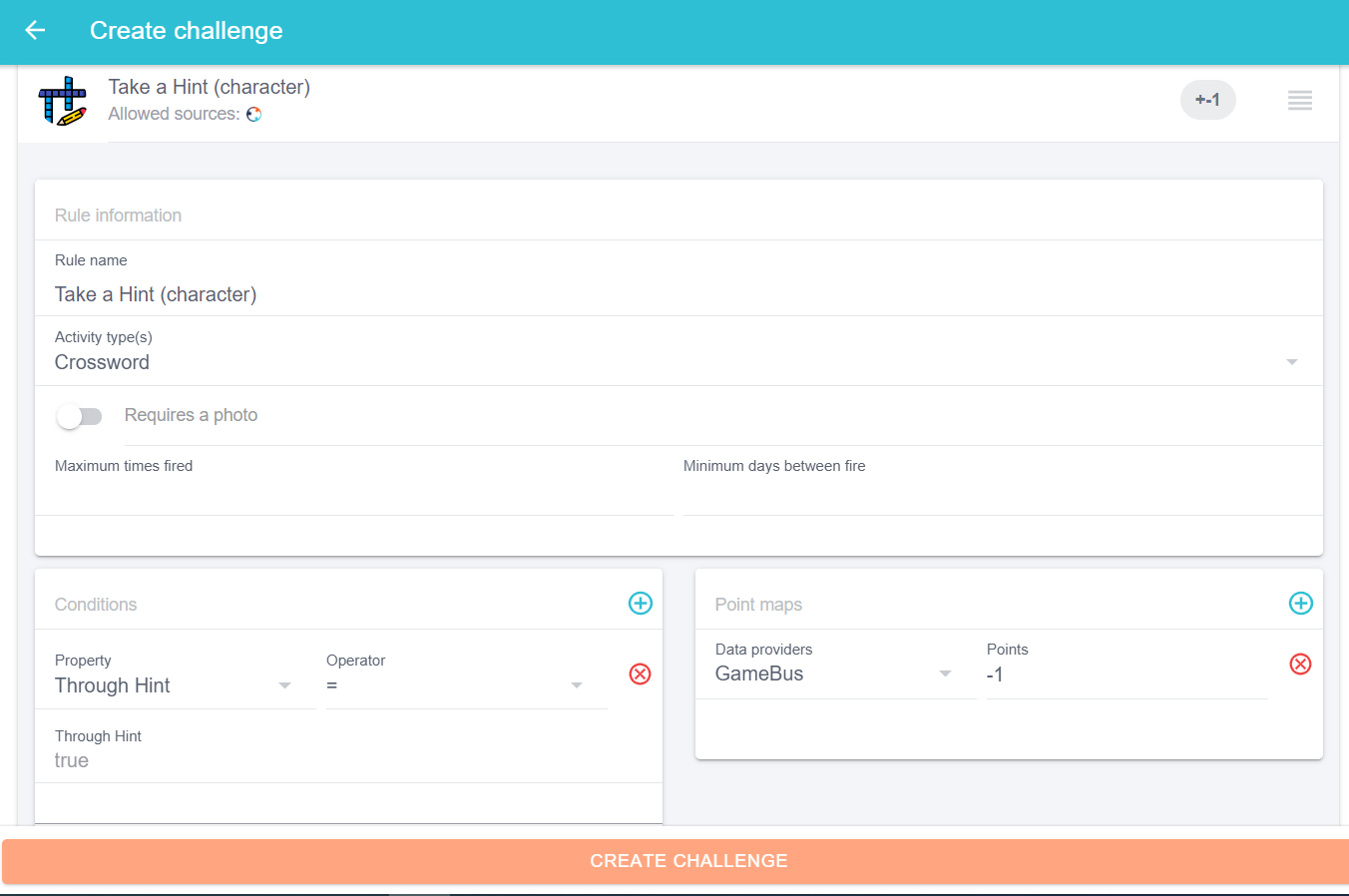
- Take a Hint: If the player takes a hint for a word, then 1 point will be reduced.
- Enter Correct Word: Upon guessing the correct word, player gains 5 points.
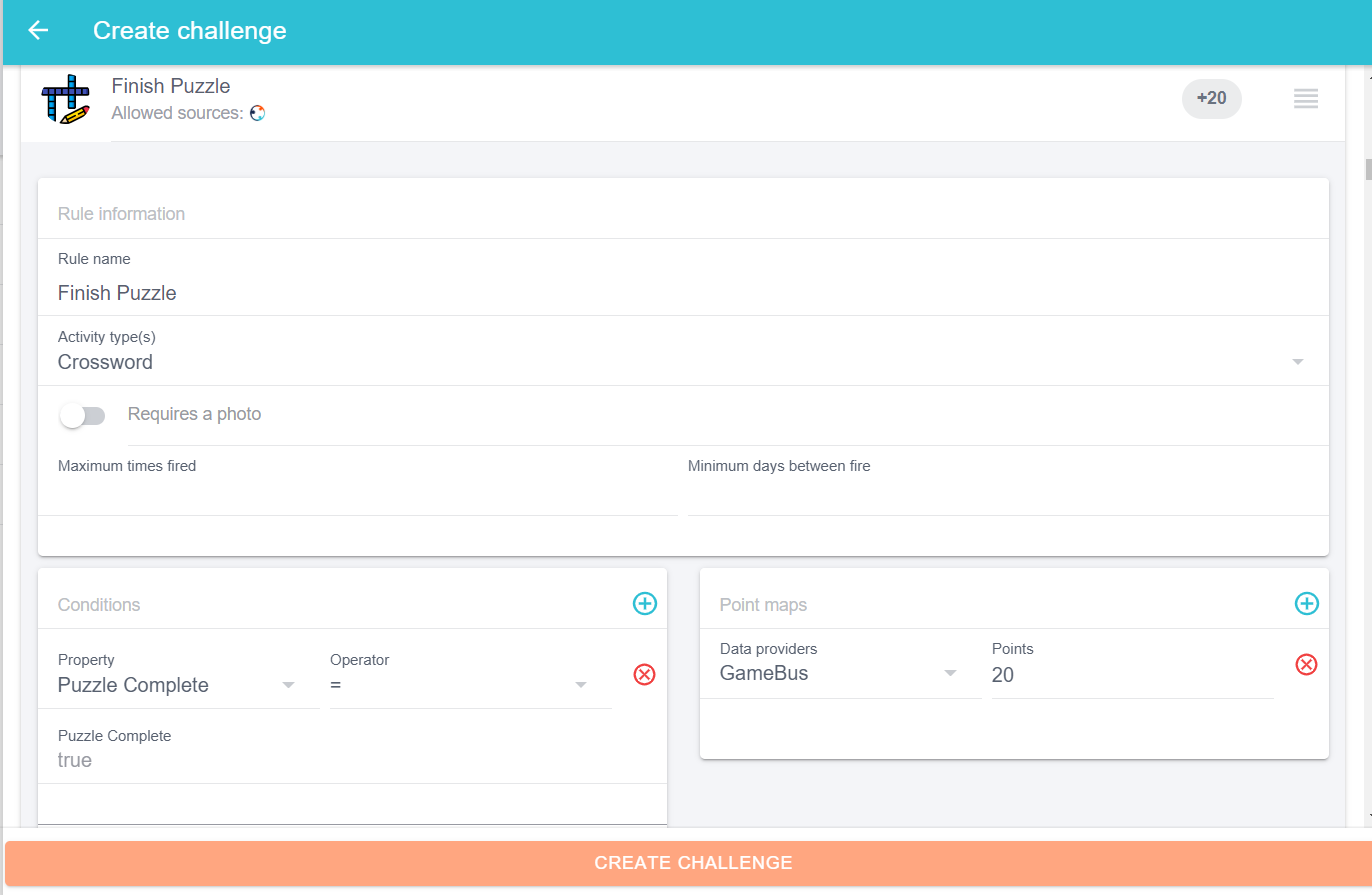
- Finish Puzzle: Upon finishing the puzzle, the player gains 20 points.
While creating a challenge, these game rules can be defined. Creating a challenge with these example game rules is illustrated in the following pictures.
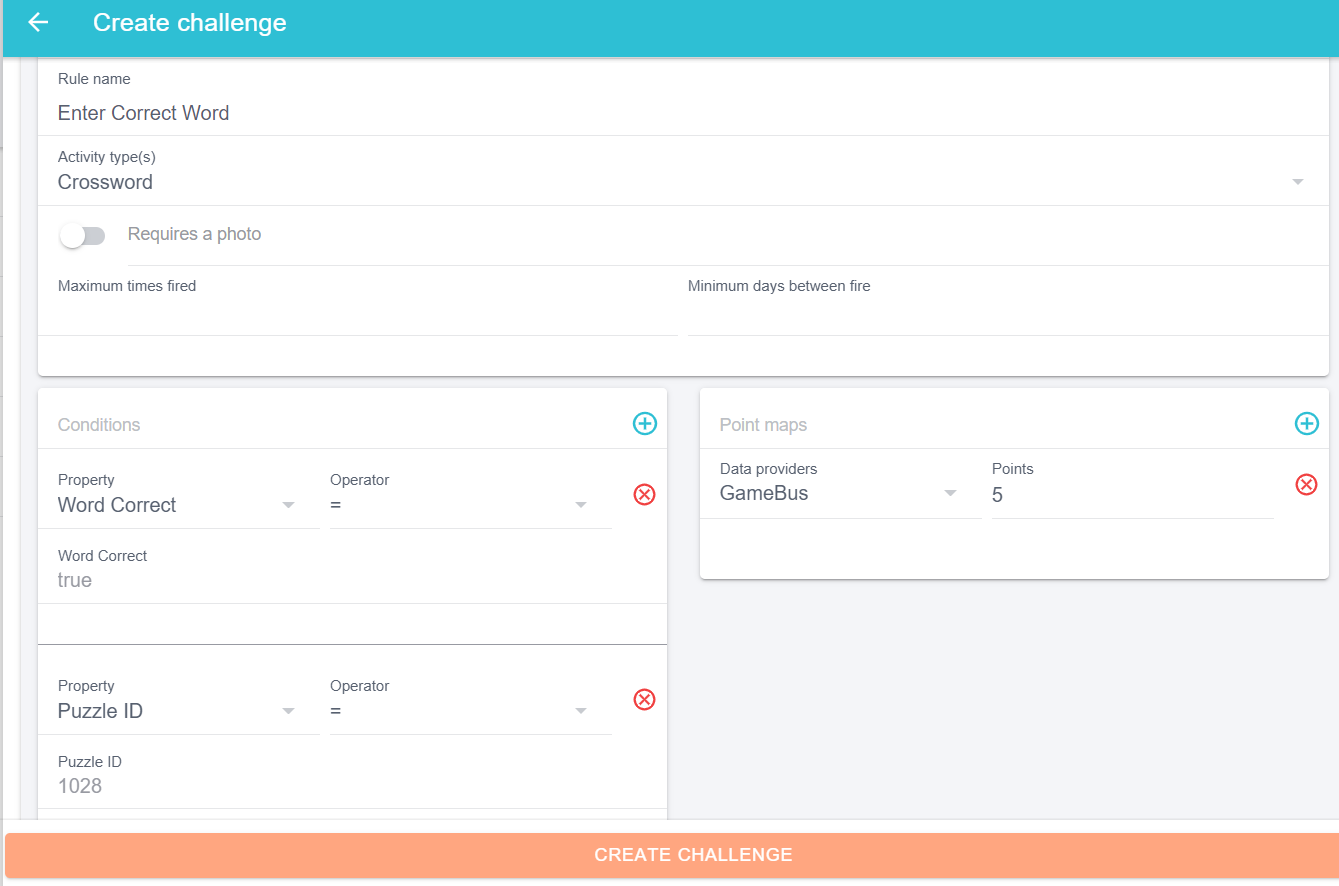
A rule can be defined by giving it a name and a correct activity type. Furthermore, “Conditions” section can be used to define the rule properties and “Point maps” section is used to define a mapping point for the rule.
- Defining the rule “Enter Correct Word”:
- Defining the rule “Take a Hint”:
- Defining the rule “Finish Puzzle”:
After the challenge is created and the player is joined to the challenge. A new activity can be created within the challenge in the “Create activity” page and in the “Rewarded Activities” tab.
It is explained in the following how these rules look like when playing the game.
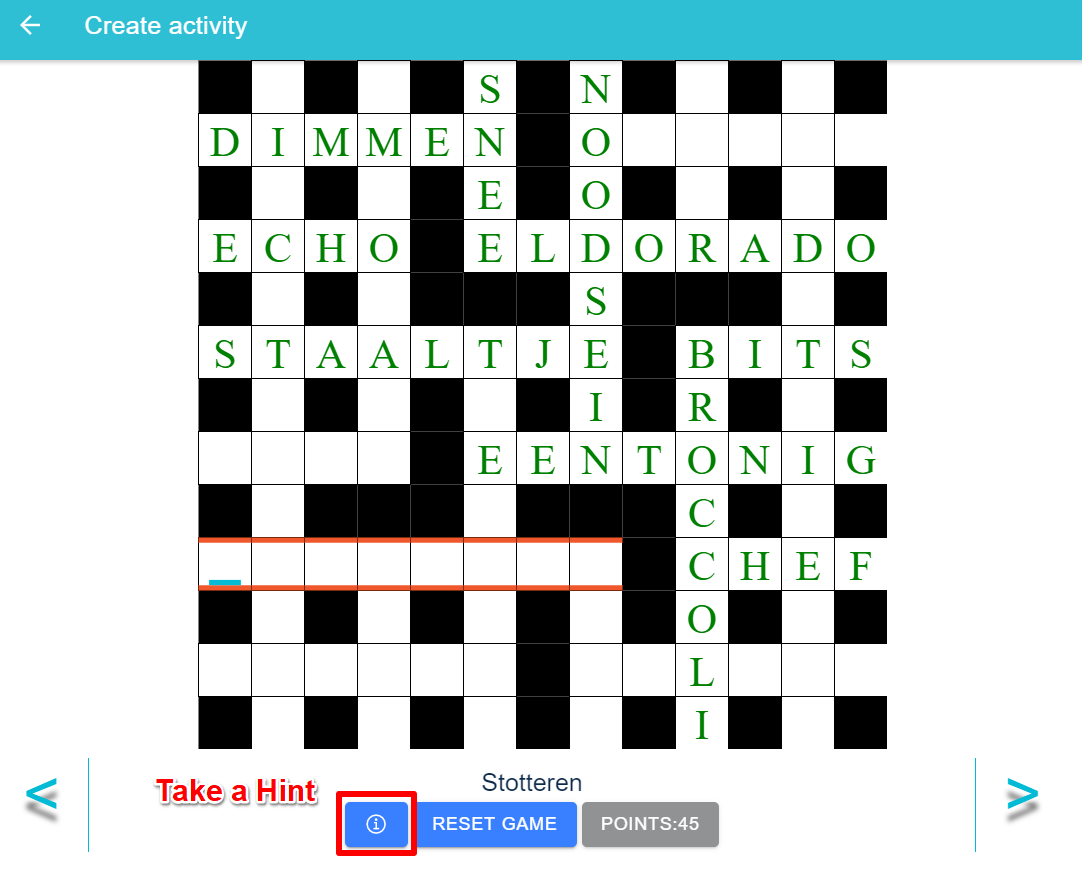
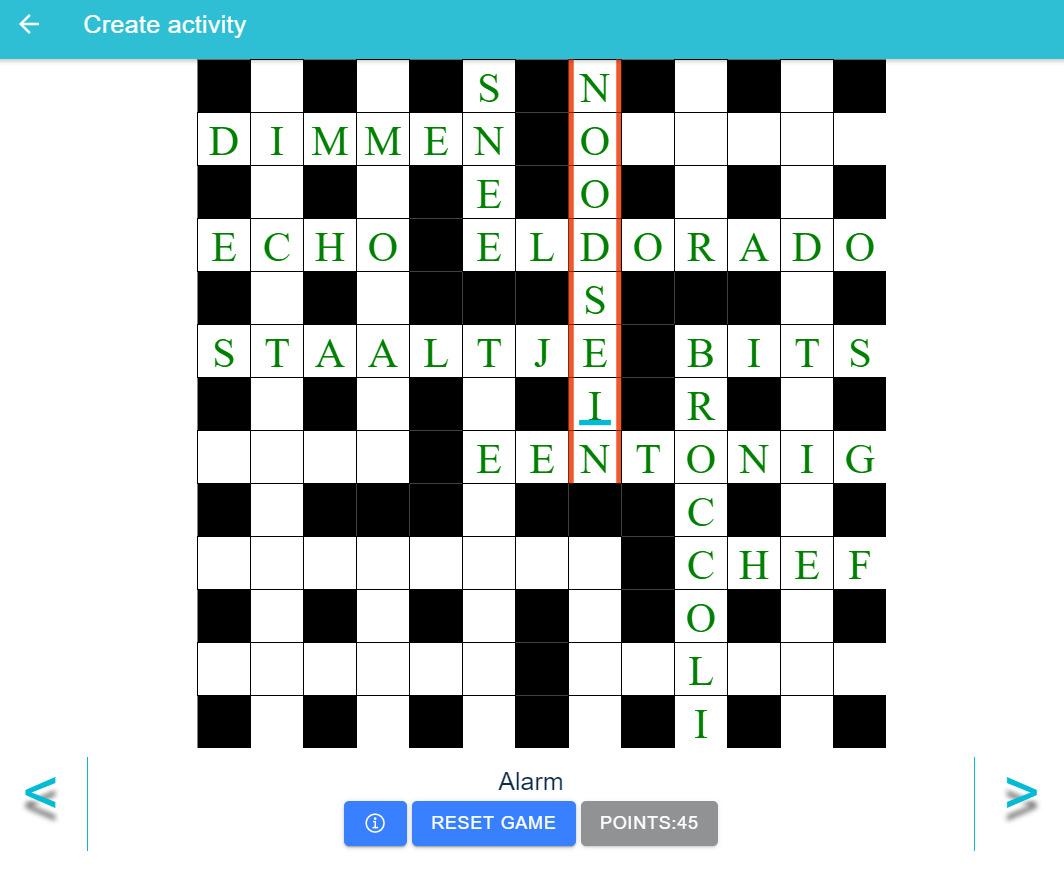
Rule 1: Take a Hint
In order to take a hint, anywhere on the square where the word is not guessed should be clicked and then press the hint button.
A hint letter for that word will be shown and the points will be reduced by 1 point.
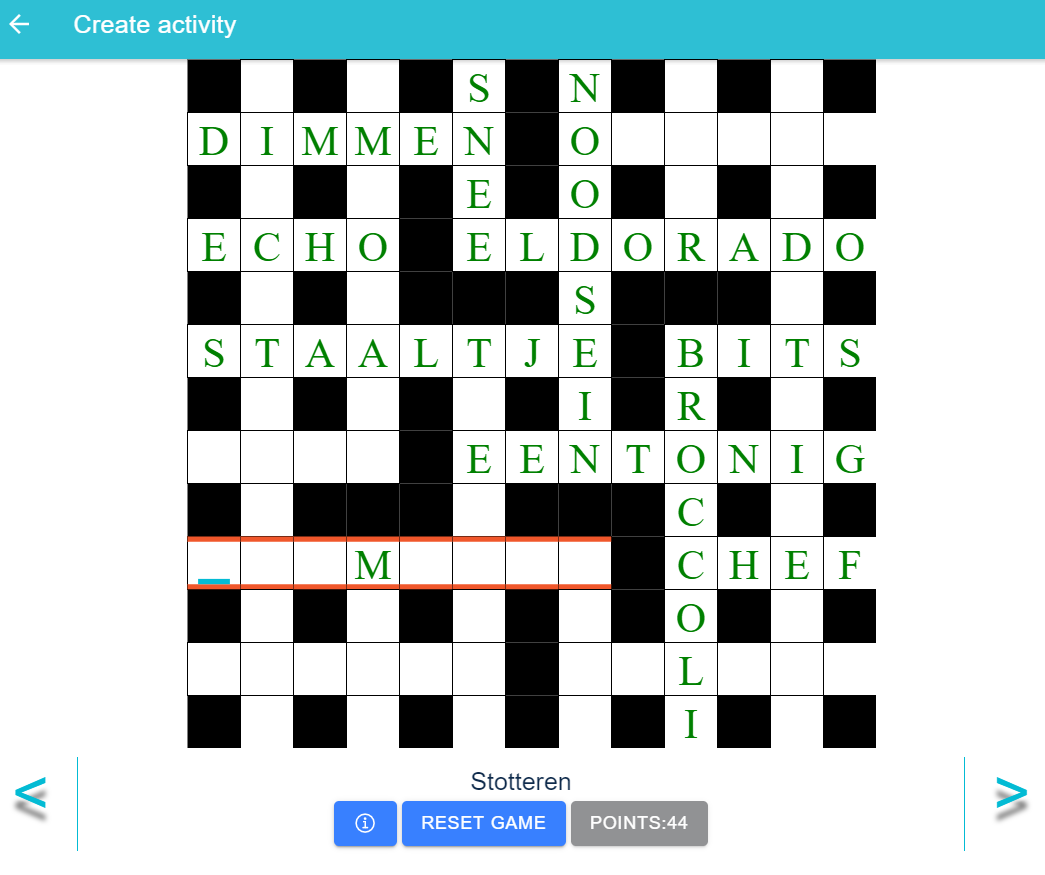
Rule 2: Enter Correct Word
For guessing the correct word, cursor should be moved to the question that the player wants to answer. You can also use the back/next arrows to change between question.
If the correct word is entered, then the player gains 5 points and the correct word is shown in green letters.
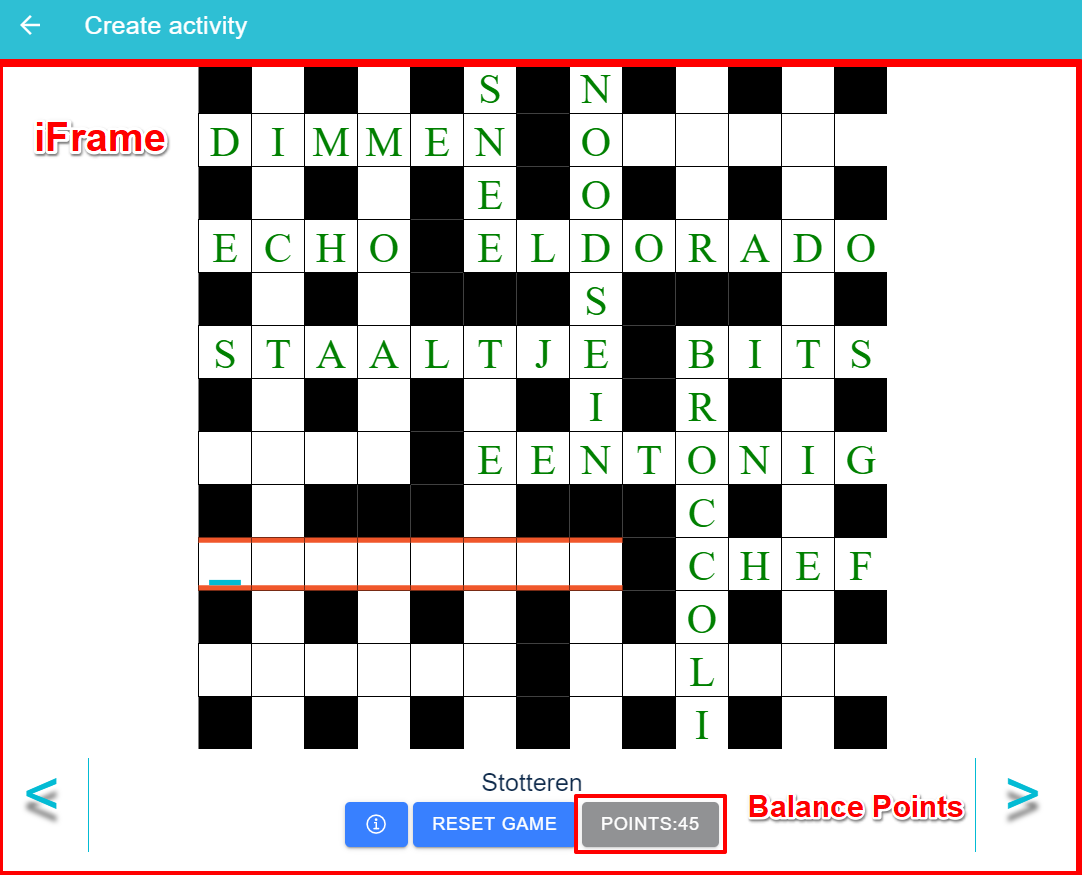
Rule 3: Finish Puzzle
Upon finishing the puzzle, the player gains 20 extra points.
Checklist for the integration of a new game
The goal in this section is to show a flow of required actions that need to be done and checked for the integration of a new mini game. Having these points, one can get a broader perspective of all required steps. Further details are provided in the following sections.
- A GameDescriptor for the mini game is created. In most cases, this is equivalent to the name of the mini game.
- All required properties for the mini game are created taking into consideration reusing of already existing properties like: “MINIGAME_DATA”, “RESET”, … (Please contact gameBus team or use the developer portal)
- All necessary property permissions are defined or granted. (Please contact gameBus team or use the developer portal)
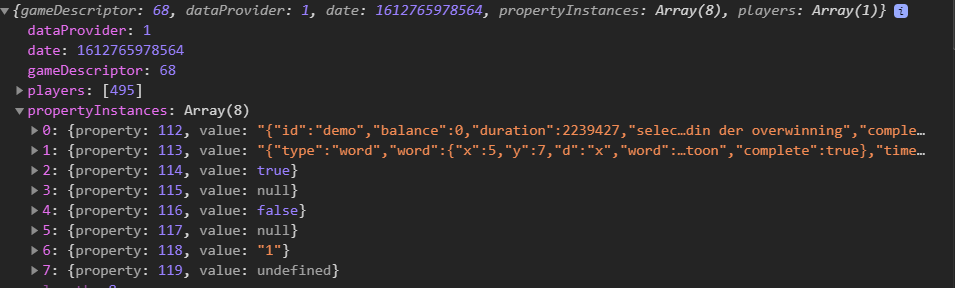
- As part of the mini game implementation, listen to message passing from parent. This message includes information about the gameDescriptor, propertyInstances, challenge, rules, conditions and so on. This information may be used then for implementation of the mini game. (please see the section “Communicated “message” between miniGame iFrame and GameBus Frontend”)
- In the mini game implementation, message should be sent to the parent upon events happening in the mini game. For that an activityForm should be defined. Then the list of activityForms should be sent to the parent. (please see the section “ActivityForm Build in the Mini Game IFrame”)
- A fixed structure is defined for GameDump. The GameDump includes the data for the game. It should be designed so that the main structure remains fixed and the values change throughout playing the game. A new propertyInstance for the property MINIGAME_DATA can be created and be patched into the ActivityForm.
- Tip for implementation: the propertyInstance for the property “MINIGAME_DATA” holds the state of the game data and can be used to retrieve the state for the mini game.
- Tip for implementation: upon events in the mini game, propertyInstances should be created and ActivityForm should be patched. Loop over all the propertyPermissions of “scheme” sent from parent in the message and set the values. Then patch these propertyInstances to the activityForm. (For an example implementation, please refer to “miniGameCrossword” project)
- If RESET is a valid functionality for the mini game. The already existing “RESET” property can be used to create a propertyInstance of ActivityForm.
- New entries in the mini game tables are added. (For more info, please contact the gameBus team) In this step, some information about the game should be provided by the developer of mini game: ** A “URL” under which the mini game can be accessed ** An initial “gameDump” string representing the initial state of the mini game. ** Information whether the game state can be rendered in a result page for each posted gameSession. Alternative is that the result page just includes information about the propertyInstances of the gameSession. ** Whether different gameDumps with regard to different complexities are available.
Cross Domain Communication
For the integration of the games, it is considered that a cross domain communication should take place. This means that the game may be hosted on a different domain comparing to GameBus. For this purpose and to be able to illustrate our crossword example, a new host is considered under the domain: minigames.gamebus.eu
The frontend integration considers using an iFrame to call the mini game (e.g: crossword game). An iFrame is an inline frame used inside a webpage to load another HTML document inside it. The main challenge here is to keep the communication between iFrame (mini game) and the parent (gamebus frontend) as simple as possible with regards to the performance. Api request calls to retrive or persist data will be handled in the parent (gamebus frontend) whereas presenting the data will be handled in the iFrame (mini game). This data includes for example the correct words that are entered so far and the updated balance points.
Minigame creates the game based on input data from the parent so called GameDumps including the game data, balance points and so on. Game creates events based on the variables in the gameDump which explain events happening in the game (e.x: word is complete or a hint is taken). In the following section, gameDump structure is explained in more detail.
Implementation
First Steps
Definitions of GameDescriptor, GameDump and Properties
Before starting with the integration, there are few preparations which are needed to be considered:
- Defining a new game descriptor
- Defining required properties
- Defining GameDump(s)
In the following, these requirements are explained in detail with respect to our crossword mini game example.
In order to integrate a new game, a few GameBus definitions should be declared which are used to define a game and persist game events. The crossword example is also here taken to explain the application.
The following json shows the “Crossword” “GameDescriptor” which is defined for the “Gamebus” “DataProvider”. And it contains required “Properties”. These properties are also explained later in this section.
A game activity can be created by choosing the game descriptor of “Crossword”. It means that for the integration of a new game, a new game descriptor for that game should be added.
(for more information how to integrate a new DataProvider with GameDescriptors and Properties, please refer to: GameBus Developer Portal )
Furthermore, the game data are defined in the form of a gameDump. The gameDump is a string and kept in the database. The initial data dump is therefore available in the miniGameState table. This initial data dump can then be retrieved again if the game is supposed to implement a reset functionality.
miniGameState table has an “id”, an integer “complexity” value for the game and a string “gameDump”. If the gameDump can be defined differently with respect to complexity of the game, then it is recommended to define more than one gameDump with different complexities. Please notice that in this case the main structure of the gameDump remains same.
In order to understand how an example gameDump can be defined, please have a look at the gameDump for the CROSSWORD.
A gameDump for the “Crossword” game contains information like list of all the words in the puzzle. Open the json file in the following to see an example gameDump. Each word in the puzzle has following attributes:
- x: horizonal position
- y: vertical position
- d: vertical or horizontal direction with values of x or y
- word: the solution word
- input: input from the player
- question: the crossword question
- complete: boolean declaring whether the player has played the word or not
Here is an example gameDump for CROSSWORD mini game:
Finally, correct properties should be available. Posting a crossword activity creates a GameSession and the related PropertyInstances for the following properties:
- MINIGAME_DATA: It stores the gameDump as value
- MINIGAMESTATE_ID: It has the MiniGameStateID as value
- COMPLEXITY: It stores the miniGameState complexity as value.
- WORD_ENTERED: It stores the new word which is entered.
- THROUGH_HINT: It stores true as value if the hint is used.
- WORD_CORRECT: It stores the new word which is correct.
- RESET: It stores true as value if the reset button is clicked.
In order to integrate a new game other than the crossword game, appropriate properties for that game need to be defined and implemented.
You should make sure that upon events in your game, you may need to instantiate the correct relevant property. Create and path propertyInstances. Create an activityForm and path all propertyInstances in it and send it to the parent. In the next section, it is described how you can create an activityForm in more detail.
Therefore as a game developer, you just need to send a list of activityForms to GameBus.
Further api calls to persist the activities will be handled on the GameBus side. This means that GameBus adds each success or event in the game as a new activity instance (gameSession). Additionally, all related propertyInstances for the defined properties will be created.
ActivityForm Build in the Mini Game IFrame
once gameDescriptor, dataProvider and properties are defined. An activity can be created. Details about the structur can be found in the following.
this.activityForm = this.fb.group({
gameDescriptor: [this.sid, Validators.compose([Validators.required])],
dataProvider: [1, Validators.compose([Validators.required])],
miniGameUse: this.miniGameUse,
date: [this.datetime.now],
propertyInstances: this.fb.array([]),
property: null,
value: null,
players: [[this.pid], Validators.compose([Validators.required])],
});
Here is an example built activityForm:
After each successful event the activityForm or list of activityForms should be sent to the parent frontend so that these activities will be posted and persisted.
For more information how you can send this message from the mini game to the parent frontend, please see the section “Communicated “message” between miniGame iFrame and GameBus Frontend”. For more information about the integration of mini game in the parent frontend and used frameworks, please refer to the section “Frontend Integration”.
Frontend Integration
The miniGame is included as an embedded iframe in the parent and exists in a different domain. It can be possible to implement the minigame with any framework keeping in mind that posting messages to the parent window is possible. Again for illustration purposes, we can have a look at how Crossword miniGame is implemented.
Please clone the repository for a closer look: https://bitbucket.org/vitalithree/minigame-crossword/src/master/
The Javascript code for Crossword is written using CANVAS Api (for more information, please see: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Canvas_API
It is then included into the html file using the canvas html tag and further necessary buttons for the game:
<div class="gameArea">
<canvas class="crossword"></canvas>
<ion-button (click)="resetGame()">Reset Game</ion-button>
...
</div>
The canvas JavaScript implementation is then implemented in the typeScript file.
Finally, the game will be initiated by calling the crossword function and passing the gameDump property sent from the parent to the iFrame.
let game = new Crossword(gameDump, document.querySelector(".gameArea"), true);
Upon pressing the reset button, message will be sent from iFrame to the parent frontend. This message is explained in more detail later.
The call sequence is declared for the event example of guessing the correct word by the player in the following diagram.
Call Sequence
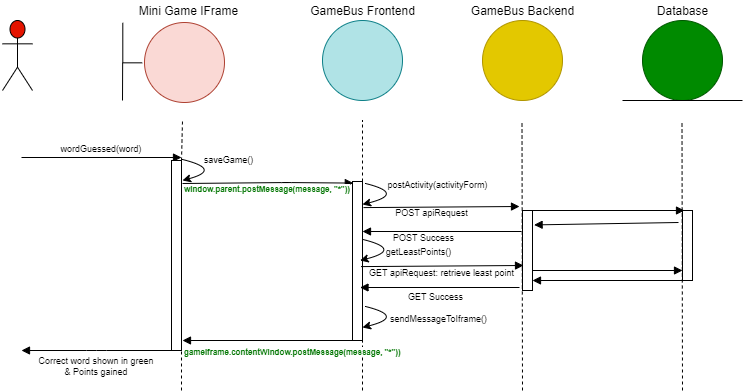
As it is also shown in the diagram, iFrame and parent GameBus frontend communicate via a json message which is declared in more detail in the following section.
In the miniGame, we should therefore implement posting the message to the parent window:
window.parent.postMessage(message, '*')
Communicated “message” between miniGame iFrame and GameBus Frontend
Depending on the mini game logic, a message should be transferred from the parent GameBus frontend to the embedded miniGame iFrame and reversely from the iFrame to the parent. In the crossword for example, message send from parent to iFrame contains the following parameters:
var message = JSON.stringify({
scheme:this.scheme,
activity:this.activity,
gameStateId:this.gameStateId,
summary:this.summary,
pid:this.pid,
game:this.game,
gameDump:this.gameDmp,
reset: this.reset,
newDump:this.newDump,
leastPoint: this.leastPoint,
miniGameUse: this.miniGameUse,
challengeId: this.cid,
activeChallengeId: this.activeChallengeId
}); ----
- scheme: contains gameDescriptor and propertyPermissions and defined in the play page of the activity
- activity: gameDescriptor and propertyPermissions and is defined only in the result page of the activity
- gameStateId: game state id referring to the MiniGameState table to retrieve the gameDump
- summary: summary contains the challenge info
- pid: player id
- game: the initiated game from gameDump
- gameDump: gameDump including game data
- reset: reset flag indicating if the message was sent after a reset
- newDump: flag to indicate if the dump has been changed
- leastPoint: balancePoints of the player calculated newly
- challengeId: the challengeId if a challenge is defined for the game
- activeChallengeId: the challengeId if an active challenge exists for the game
And the message from iFrame back to the parent contains the following parameters:
const message = JSON.stringify({
activityForms:this.activityForms
});
- activityForms: list of activityForms which should be persisted at the parent side
In order to post the message, the regarding post in the mini game should be implemented which posts a message to the parent for further processing. This processing may include api request calls to the GameBus backend which are included in the parent project.
window.parent.postMessage(message, '*');
Crossword was just chosen as an example to be able to explain the case better. However, one should think in terms of the game which should be integrated and find out which parameters should be included in the communicated message. However, for example the good practice is that the game always listens to the gameDump coming from the parent which is retrieved from database. Following by persisting each activity, the balance points should be calculated newly and be sent to the mini game again. The reason is that other activities other than game like walking, running and so on can also change the balance points. Furthermore, mini game should include the activityForms which should be posted in the message to the parent. So that each activity is then persisted via api requests which are in the parent project.
References
- Shahrestani, A., Van Gorp, P., Le Blanc, P., Greidanus, F., de Groot, K., & Leermakers, J. (2017, July). Unified health gamification can significantly improve well-being in corporate environments. In 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC) (pp. 4507-4511). IEEE.